The whole purpose of exFAT was to allow easy transfer of large files between platforms in a format that didn't require third party drivers on either the Mac or Windows to read the drive. To make sense of why MS would cut off the use of exFAT for internal hard drives, it has to be understood that exFAT still doesn't have a final specification. Microsoft's successor to FAT32, exFAT, is compatible with recent versions of Windows and Mac OS and removes the 4GB limitation, but brings its own set of trade-offs (see Resources). Formatting From.
File system formats available in Disk Utility on Mac. Disk Utility on Mac supports several file system formats: Apple File System (APFS): The file system used by macOS 10.13 or later. Mac OS Extended: The file system used by macOS 10.12 or earlier. MS-DOS (FAT) and ExFAT: File systems that are compatible with Windows. Open Disk Utility for me.
TL;DR version
For Mac OS X to read-write exFAT formatted HDD, two options
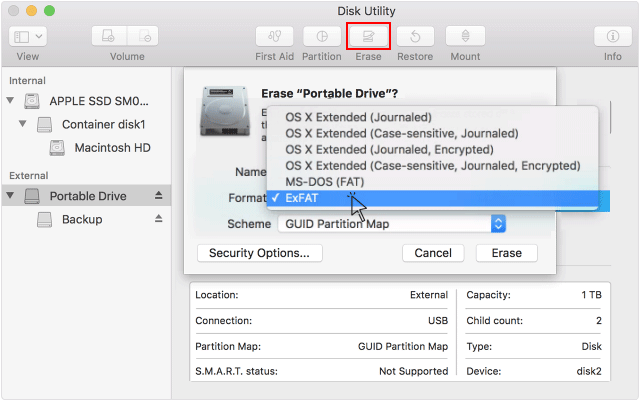
- Format using Mac:
- Disk Utility ->
- Erase ->
- choose exFAT ->
- OK
- Format using Windows:
- My Computer ->
- Right Click HDD ->
- Format ->
- choose exFAT ->
- AUS 128 kilobytes->
- Start
Background
Turns out exFAT exists so that Mac and Windows can co-exist harmoniously. There are many forum discussions and how-toarticlesoutthererecommending exFAT if you want to share files between Mac and Windows.
What most of them failed to mention is the correct allocation unit size / cluster size necessary for the harmonious relationship to work. Most of them talked about what the allocation unit size does, which might be misleading for the purpose of getting it up and running seamlessly.
My Story
I want to use an external HDD as the scratch disk for a video editing project on a Mac OS X 10.7.5. But my files are on my Windows 8.1 laptop HDD, which was formatted in NTFS. By default, Mac OS X can only read but not write to NTFS HDD. Google mac management tools. Of course there are NTFS read-write solutions out there for Mac. Among them Tuxera NTFS, Paragon NTFS, or NTFS-3G FUSE.
Disclaimer: I have not tried Tuxera or Paragon. I used NTFS-3G FUSE from 2009-2013 on my Macbook Snow Leopard, so far so good. I have not tried it on later versions of Mac OS X. Mac format usb stick fat32. There is a high chance of it not working on OS X 10.7 and later (see Known Issues).
Then I found out that if I format the HDD in exFAT, it should work for both Windows and OS X. I figured that since most of my files are videos with BIG file sizes, I chose 4096 kilobytes for the AUS. It formatted nicely. But lo and behold, OS X doesn't even recognize the HDD. I tried to force mount it but nope, it doesn't work.
So I figured that if I use OS X's Disk Utility to format, it should work for both Mac and Windows. This time it works! Turns out Disk Utility formatted the HDD with 128 kilobytes AUS (131072 bytes divide by 1024).
Mac master tool set. Just for kicks, I used Windows to format it again with AUS 128 kilobytes. Yeap, it works.
Conclusion
128 kilobytes is the harmonious constant between Windows and Mac OS X 10.7.5. Use 128 kilobytes AUS while formatting a HDD so that it works for both Windows and Mac OS X.
Disk Utility User Guide
Disk Utility on Mac supports several file system formats:
Exfat For Mac
Apple File System (APFS): The file system used by macOS 10.13 or later.
Mac OS Extended: Is there outlook for mac. Jixipix pastello pro 1 1 119. The file system used by macOS 10.12 or earlier.
MS-DOS (FAT) and ExFAT: File systems that are compatible with Windows.
Apple File System (APFS)

Apple File System (APFS)
Apple File System (APFS), the default file system for Mac computers using macOS 10.13 or later, features strong encryption, space sharing, snapshots, fast directory sizing, and improved file system fundamentals. While APFS is optimized for the Flash/SSD storage used in recent Mac computers, it can also be used with older systems with traditional hard disk drives (HDD) and external, direct-attached storage. macOS 10.13 or later supports APFS for both bootable and data volumes.
APFS allocates disk space within a container (partition) on demand. When a single APFS container has multiple volumes, the container's free space is shared and is automatically allocated to any of the individual volumes as needed. If desired, you can specify reserve and quota sizes for each volume. Each volume uses only part of the overall container, so the available space is the total size of the container, minus the size of all the volumes in the container.
Choose one of the following APFS formats for Mac computers using macOS 10.13 or later.
APFS: Uses the APFS format. Choose this option if you don't need an encrypted or case-sensitive format.
APFS (Encrypted): Uses the APFS format and encrypts the volume.
APFS (Case-sensitive): Uses the APFS format and is case-sensitive to file and folder names. For example, folders named 'Homework' and 'HOMEWORK' are two different folders.
APFS (Case-sensitive, Encrypted): Uses the APFS format, is case-sensitive to file and folder names, and encrypts the volume. For example, folders named 'Homework' and 'HOMEWORK' are two different folders.
You can easily add or delete volumes in APFS containers. Each volume within an APFS container can have its own APFS format—APFS, APFS (Encrypted), APFS (Case-sensitive), or APFS (Case-sensitive, Encrypted).
Exfat Compatible With Mac
Mac OS Extended
Choose one of the following Mac OS Extended file system formats for compatibility with Mac computers using macOS 10.12 or earlier.
Mac OS Extended (Journaled): Uses the Mac format (Journaled HFS Plus) to protect the integrity of the hierarchical file system. Choose this option if you don't need an encrypted or case-sensitive format.
Mac OS Extended (Journaled, Encrypted): Uses the Mac format, requires a password, and encrypts the partition.
Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled): Uses the Mac format and is case-sensitive to folder names. For example, folders named 'Homework' and 'HOMEWORK' are two different folders.
Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled, Encrypted): Uses the Mac format, is case-sensitive to folder names, requires a password, and encrypts the partition.
Windows-compatible formats
Choose one of the following Windows-compatible file system formats if you are formatting a disk to use with Windows.
MS-DOS (FAT): Use for Windows volumes that are 32 GB or less.
ExFAT: Use for Windows volumes that are over 32 GB.
